Various after finishing processes:
1. preshrinking
Preshrinkage is the process of physically reducing the shrinkage of fabric after soaking in water to reduce the shrinkage rate. Mechanical pre-shrinkage is the fabric first by steam or spray to wet, and then by mechanical extrusion, so that the warp wave height increases, and then by loose drying

2. Stenter
Tensioning is the process of making use of the plasticity of cellulose, silk, wool and other fibers under wet conditions to gradually widen the width of the fabric to the specified size for drying, so that the shape of the fabric can be stable, also known as fixed finishing.

3. Sizing
Sizing refers to the finishing process in which the fabric is dipped in slurry and dried to obtain a thick and stiff feel.
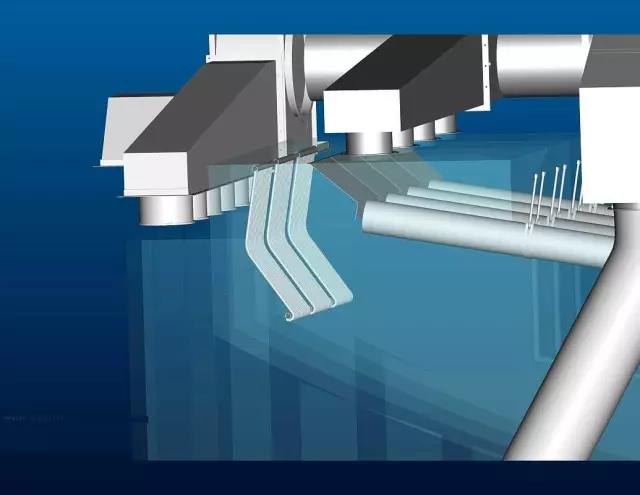
4.Heat setting
Thermal setting is the process of making thermoplastic fiber and blend or interweave relatively stable, mainly used for the processing of synthetic fibers such as nylon or polyester and their blends, which are easy to shrink and deform after being heated. The fabric after heat setting can improve dimensional stability and feel more stiff.

5. Whitening
Whitening is the use of light complementary principle to increase the whiteness of the textile process, also known as whitening. There are two whitening methods: blue and fluorescent whitening.

6. Calendering, electro-gloss and rolling
- Rolling light is the process of using the plasticity of fibers in hot and humid conditions to roll the surface of the fabric flat or roll out the parallel fine twill to enhance the luster of the fabric.
- Flat rolling is composed of hard roll and soft roll. After rolling, the yarn is flattened, the surface is smooth, the luster is enhanced, and the feel is stiff.
- Soft rolling light is composed of two soft rollers. After rolling, the yarn is slightly flat, with soft luster and soft feel.
7. Peach finish and nubuck finish
The process of grinding the surface of the fabric with sand grinding roller (or belt) into a layer of short and dense nap is called flocking, also known as wool grinding, wool finishing can make the warp and weft yarn at the same time to produce nap, and the nap is short and dense.
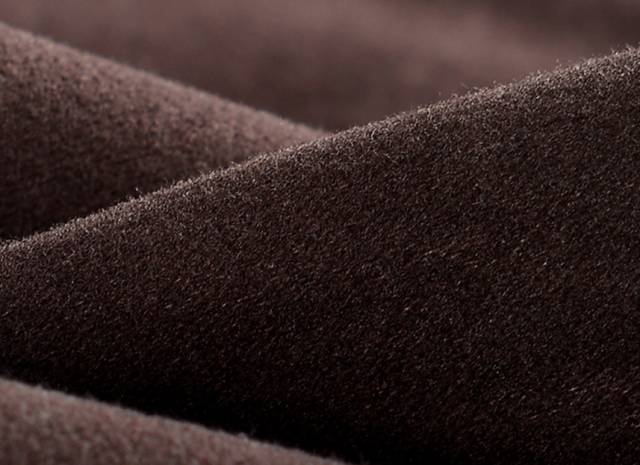

8. Fuzz
Fuzz is a process in which dense needles or thorns pick up the fibers on the surface of the fabric to form a layer of fluff, also known as drawing finish. Fuzz is mainly used in woolen fabric, acrylic fabric and cotton fabric. The fluffy layer improves the warmth of the fabric, improves its appearance and makes it feel soft.

9. Shearing
Shearing is the process of removing unwanted hairs from the surface of fabric with a shearing machine. Its purpose is to make fabric weave clear, the surface is smooth, or make fuzz, fuzz weave or suede neat. Wool, velvet, artificial fur and carpet products need shearing.

10. Soft
There are two methods of mechanical finishing and chemical finishing. Mechanical finishing is achieved by rubbing and bending the fabric for many times, and the soft effect is not ideal after finishing. Chemical soft finishing is to apply softener on the fabric, reduce the friction coefficient between fiber and yarn, so as to obtain soft, smooth feel, and finishing effect is remarkable.